Sustainability governance
The main purpose of all governance at SCA is to guarantee the Group’s commitments to its stakeholders: shareholders, customers, employees, suppliers, lenders and communities.
Sustainability governance
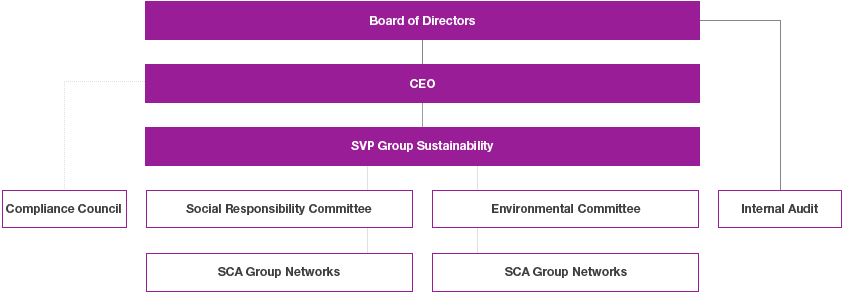
SCA’s Executive Management Team bears the overall responsibility for the control of SCA’s business in the sustainability field.
SCA has a Group Function in charge of sustainability, led by the Senior Vice President Group Sustainability, who reports to the CEO and is a member of the Executive Management Team. Apart from social and environmental affairs, the function is also responsible for SCA’s public affairs and its compliance function. In close collaboration with the business unit presidents, the approved strategy and objectives are broken down into specific targets and activities to ensure compliance with the Group’s objectives and business plans.
The Environmental Committee and the Social Responsibility Committee draft proposals for policies and principles for governing the sustainability work, as well as objectives and action programs at Group level. They also coordinate and follow up the Group’s initiatives and objectives in the environmental and social area. The Social Responsibility Committee is responsible for preparing documentation regarding management of human rights. Conclusions and proposed actions are reported to SCA’s Compliance Council and the President and Board of Directors, who approve the strategic priorities and objectives. The committees include members of all business units and representatives of the Sustainability, Human Resources, Communications and Legal Group Functions.
The Compliance Council consists of SCA’s CEO (attends twice a year), SVP Group Human Resources, SVP Group Sustainability (chair), General Counsel, VP Compliance and Ethics, VP Internal Audit and business unit presidents by invitation. The Compliance Council will ensure an effective SCA Group compliance framework and program and secure a systematic approach to implementation. It oversees implementation of and compliance with SCA’s Code of Conduct and other Group policies.
Responsibility for implementation rests with the operational organization. A number of networks operate horizontally across SCA’s different business units to guarantee a consistent approach.
Corporate Governance at SCA

SCA Group networks
Water management network: Establishes the Group’s aspiration level for reductions in emissions and water usage. The network also analyzes the impact of the EU’s Water Framework Directive on SCA’s operations.
FSC® network: Disseminates information on responsible forest management throughout the organization, and coordinates the Group’s position and activities in relation to the FSC.
RMS network: Compiles information and makes calculations and presentations relating to resource use and environmental data.
Chemicals management network: Leads and supports development for harmonized chemical procedures and proposes group policies, priorities and objectives.
ESAVE network: Coordinates the Group’s projects aimed at reducing SCA’s energy consumption and environmental impact.
Energy network: Identifies cost-efficient solutions and synergies in connection with energy sourcing. The network also handles emissions trading.
Public Affairs network: Leads and coordinates the work aimed at influencing legislation, decisionmakers and stakeholders in prioritized areas with potential impact on SCA’s operations.
Health and Safety network: Proposes goals and activities, follows up initiatives and highlights health and safety best practices.
Supplier Code of Conduct network: Identifies ethical and social supply chain risks.
Monitoring
In addition to being reviewed by SCA’s external auditors, its operations are subject to external reviews and monitoring by, among others, the Swedish Financial Supervisory Authority and Nasdaq Stockholm. Life cycle assessments are another example of third-party assessments.
SCA’s own control systems include segregation of duties in critical processes and defined management responsibilities with regard to internal control. There is also a separate internal audit function at SCA that works to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of SCA’s governance processes, risk management and internal control. SCA’s Internal Audit organization contributes to the maintenance of high standards of business practice and is involved in the monitoring of Code of Conduct compliance through such activities as Code of Conduct audits at manufacturing sites and Business Practice audits. To support its work, the Internal Audit unit has a number of steering documents and policies.
Risk and risk management
SCA is exposed to various risks with a greater or lesser potential impact on the Group. The responsibility for long-term and overall management of material risks follows the company’s delegation scheme, from the Board to the President, and from the President to the business unit presidents.
A description of the most significant risks that impact SCA’s ability to achieve its established targets and its risk management is presented in chapter Risks and risk management of the 2016 Annual Report.
Corporate Governance Report
The complete Corporate Governance Report is available on SCA’s website and in the 2016 Annual Report.
SCA’s sustainability governance